Volume 12, Issue 4 (1-2018)
Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing 2018, 12(4): 430-445 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Imanzadeh A, Hamrahzdeh M. Identification of Facilitators and Deterrents of the Quality of Life in Elderly Women and Men: A Phenomenological Research. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing 2018; 12 (4) :430-445
URL: http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-1248-en.html
URL: http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-1248-en.html
1- Department of Education, Faculty of Education and Psychology, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran.
2- Department of Education, Faculty of Education and Psychology, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran. ,melika.hamrahzdeh@yahoo.com
2- Department of Education, Faculty of Education and Psychology, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran. ,
Full-Text [PDF 4149 kb]
(5160 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (9378 Views)
Full-Text: (7763 Views)
Extended Abstract
1. Objectives
The growth of elderly population is one of the most important economic, social, and health challenges of the 21st century [1, 2], and identifying the factors affecting aging-related issues is as important as for other age groups [3]. The increasing population of older adults is so remarkable that it has been described as the quiet revolution [4]. Quality of life as a health concept has an inverse relationship with all causes of death [5]. Although the changes caused by aging are inevitable, we can prevent or postpone many of them to some extent [6]. Therefore, the necessity and importance of more exploration in this field are evident. In this regard, we attempted to identify the facilitators and deterrents of the quality of life in elderly people in Pars-Abad and Moghan cities and propose appropriate solutions to address the weaknesses and problems at the old age.
2. Methods & Materials
The present research is a qualitative phenomenological study. The study population included all older adults in different regions of Pars-Abad City. Cluster random sampling method was used to recruit the samples. For this purpose, four districts (Fajr, Bakeri, Valiasr, and Shahid Motahhari) of the city were randomly selected. Then, the public places (mosques, parks, green spaces, sports venues, and shopping centers) were identified, and the researcher visited those places to select study subjects from each public place, provided that they have the inclusion criteria and willingness to participate in the research.
The data were collected through in-depth interviews. An interview guide was used in this study that prevents waste of time and energy. A total of 23 interviews were performed, each lasted from 15 to 40 minutes depending on the willingness of the interviewee to continue the conversation. The interview began with a general question about the daily life experiences of the elderly and how they see the old age and talking about it, and then more questions were asked. To interpret and analyze the data, the method of Streubert and Carpenter was used. An expert in qualitative research was consulted to analyze the data. The responses of the interviewees were compared with the findings of similar studies. Furthermore, this research is a part of the dissertation entitled “Quality of Life of the Elderly of Ardabil Province” being drafted by the researchers at the Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences of Tabriz University.
3. Results
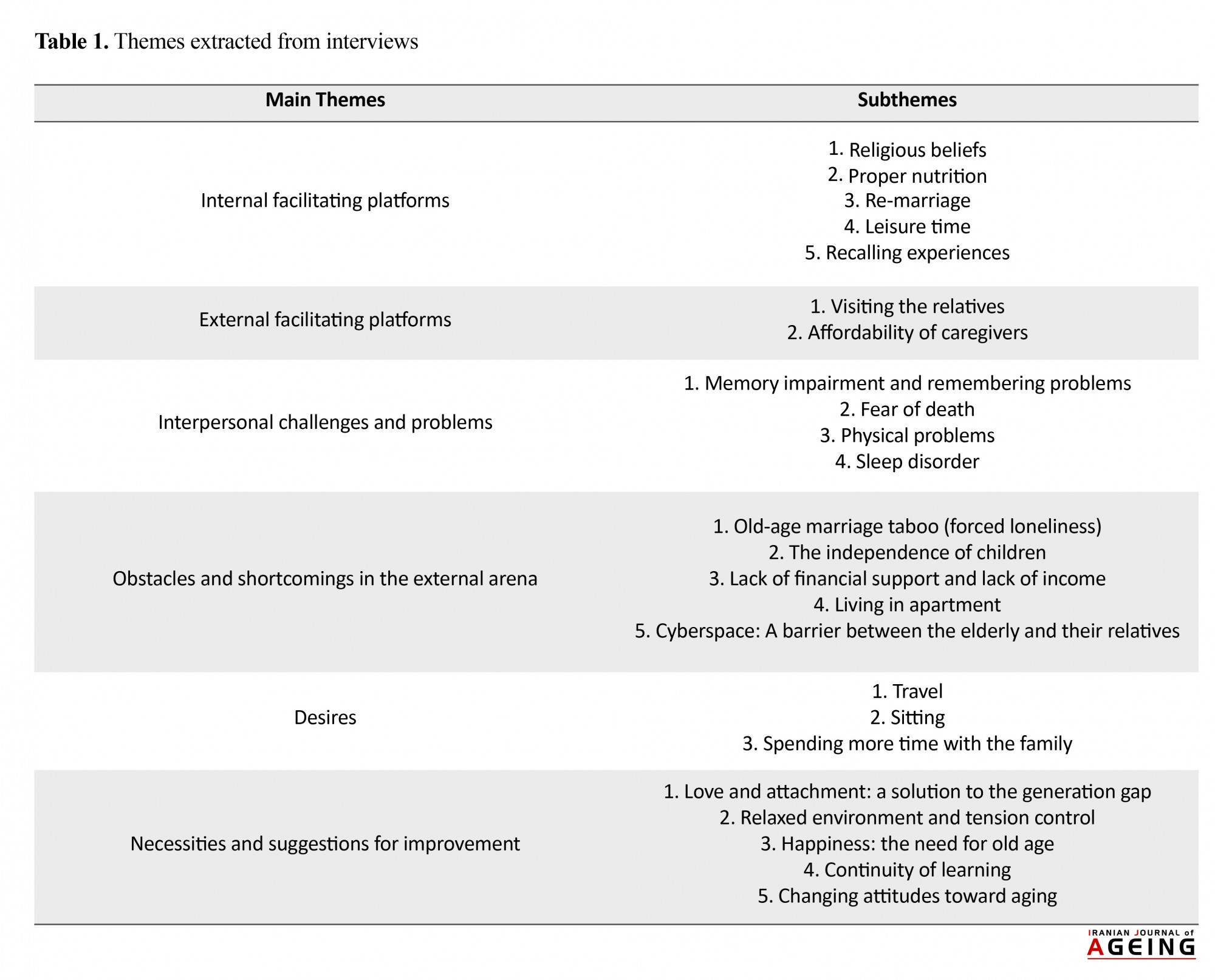
In this study, 6 main themes and 24 subthemes (Table 1) were extracted as follows:
1. Objectives
The growth of elderly population is one of the most important economic, social, and health challenges of the 21st century [1, 2], and identifying the factors affecting aging-related issues is as important as for other age groups [3]. The increasing population of older adults is so remarkable that it has been described as the quiet revolution [4]. Quality of life as a health concept has an inverse relationship with all causes of death [5]. Although the changes caused by aging are inevitable, we can prevent or postpone many of them to some extent [6]. Therefore, the necessity and importance of more exploration in this field are evident. In this regard, we attempted to identify the facilitators and deterrents of the quality of life in elderly people in Pars-Abad and Moghan cities and propose appropriate solutions to address the weaknesses and problems at the old age.
2. Methods & Materials
The present research is a qualitative phenomenological study. The study population included all older adults in different regions of Pars-Abad City. Cluster random sampling method was used to recruit the samples. For this purpose, four districts (Fajr, Bakeri, Valiasr, and Shahid Motahhari) of the city were randomly selected. Then, the public places (mosques, parks, green spaces, sports venues, and shopping centers) were identified, and the researcher visited those places to select study subjects from each public place, provided that they have the inclusion criteria and willingness to participate in the research.
The data were collected through in-depth interviews. An interview guide was used in this study that prevents waste of time and energy. A total of 23 interviews were performed, each lasted from 15 to 40 minutes depending on the willingness of the interviewee to continue the conversation. The interview began with a general question about the daily life experiences of the elderly and how they see the old age and talking about it, and then more questions were asked. To interpret and analyze the data, the method of Streubert and Carpenter was used. An expert in qualitative research was consulted to analyze the data. The responses of the interviewees were compared with the findings of similar studies. Furthermore, this research is a part of the dissertation entitled “Quality of Life of the Elderly of Ardabil Province” being drafted by the researchers at the Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences of Tabriz University.
3. Results
In this study, 6 main themes and 24 subthemes (Table 1) were extracted as follows:
Internal facilitating platforms
The subthemes extracted from the main theme of internal facilitating platforms are as follows: religious beliefs, proper nutrition, re-marriage, leisure, and recalling experiences. No one overlooks the role of religion and religious beliefs and its positive impact. Nutrition plays an important role as a supportive factor for the body and soul. One of the problems of the elderly is the death of their wife and their loneliness afterwards. Planning for recreation and leisure activities is a requirement of aging. Recalling old experiences also plays an important role in supporting mental health.
External facilitating platforms
The subthemes extracted from this theme include visiting relatives and affordability of caregivers. Personal contacts between family members and friends have a great impact on the mental health of the elderly. The role of caregivers is also important in the life of the older adults.
Interpersonal challenges and problems
The subthemes extracted from this theme are as follows: memory impairment and remembering problems, the anxiety of death, physical problems, and sleep disorders. In general, the likelihood of forgetfulness increases with the increase in age. Fear of death is a natural fear, and reduced physical abilities can affect people’s health. Mental health depends on how people acquire their basic needs. Sleep is considered as one of the most vital physical, mental, and emotional needs of human.
Obstacles and shortcomings in the external arena
The subthemes extracted from this concept are as follows: old-age marriage taboo (forced loneliness), independence of children, lack of financial support and income deficits, living in an apartment, and the cyberspace. The death of a spouse greatly increases the loneliness of the elderly. One of the problems of the elderly is the marriage of children and separation from them. Financial and therapeutic support is an effective factor in healing the mental health of the elderly. The living environment is another factor influencing the spirit of the elderly as with the introduction of new technologies into the family, there are gaps between the family members.
Desires
The subthemes extracted from this theme are as follows: travel, sitting, spending more time with the family. Trips and healthy recreation leave humans out of their routine. Sitting jobs and lack of mobility are the most probable reasons for muscle weakness and physical burnout. Assigning more time by parents and, in particular, the father, to be with the family will help the elderly.
Necessities and suggestions for improvement
In the final section, some suggestions were extracted from the words of the elderly; Love and attachment: a solution to the generation of the gap, relaxed environment and tension control, happiness: the need for old age, continuity of learning, and changing attitude towards old age.
4. Conclusion
The present study indicates that some factors contribute to improve the lives of the elderly. Internal factors such as religious beliefs, proper nutrition, re-marriage, recreation, and leisure time with exercise and music help in improvement in the quality of life of elderly. Obstacles and problems that play a deterring and negative role in the elderly are considered as internal factors which include memory impairment and remembering problems, anxiety of death, physical impairment and sleep disorders, whereas old age marriage taboo, children’s independence, lack of financial support and income deficit, living in apartment and cyberspace are considered as external factors that prevent improvement in old age. Most of the older adults have mentioned more surfing, more physical activity in their young age, and the possibility of spending more time with their families. They were also offered suggestions for a relaxed environment, love and attachment, happy life, and continuity of learning.
Acknowledgments
This research was extracted from the thesis of the second author in the Department of Education, Faculty of Education and Psychology, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
References
The subthemes extracted from the main theme of internal facilitating platforms are as follows: religious beliefs, proper nutrition, re-marriage, leisure, and recalling experiences. No one overlooks the role of religion and religious beliefs and its positive impact. Nutrition plays an important role as a supportive factor for the body and soul. One of the problems of the elderly is the death of their wife and their loneliness afterwards. Planning for recreation and leisure activities is a requirement of aging. Recalling old experiences also plays an important role in supporting mental health.
External facilitating platforms
The subthemes extracted from this theme include visiting relatives and affordability of caregivers. Personal contacts between family members and friends have a great impact on the mental health of the elderly. The role of caregivers is also important in the life of the older adults.
Interpersonal challenges and problems
The subthemes extracted from this theme are as follows: memory impairment and remembering problems, the anxiety of death, physical problems, and sleep disorders. In general, the likelihood of forgetfulness increases with the increase in age. Fear of death is a natural fear, and reduced physical abilities can affect people’s health. Mental health depends on how people acquire their basic needs. Sleep is considered as one of the most vital physical, mental, and emotional needs of human.
Obstacles and shortcomings in the external arena
The subthemes extracted from this concept are as follows: old-age marriage taboo (forced loneliness), independence of children, lack of financial support and income deficits, living in an apartment, and the cyberspace. The death of a spouse greatly increases the loneliness of the elderly. One of the problems of the elderly is the marriage of children and separation from them. Financial and therapeutic support is an effective factor in healing the mental health of the elderly. The living environment is another factor influencing the spirit of the elderly as with the introduction of new technologies into the family, there are gaps between the family members.
Desires
The subthemes extracted from this theme are as follows: travel, sitting, spending more time with the family. Trips and healthy recreation leave humans out of their routine. Sitting jobs and lack of mobility are the most probable reasons for muscle weakness and physical burnout. Assigning more time by parents and, in particular, the father, to be with the family will help the elderly.
Necessities and suggestions for improvement
In the final section, some suggestions were extracted from the words of the elderly; Love and attachment: a solution to the generation of the gap, relaxed environment and tension control, happiness: the need for old age, continuity of learning, and changing attitude towards old age.
4. Conclusion
The present study indicates that some factors contribute to improve the lives of the elderly. Internal factors such as religious beliefs, proper nutrition, re-marriage, recreation, and leisure time with exercise and music help in improvement in the quality of life of elderly. Obstacles and problems that play a deterring and negative role in the elderly are considered as internal factors which include memory impairment and remembering problems, anxiety of death, physical impairment and sleep disorders, whereas old age marriage taboo, children’s independence, lack of financial support and income deficit, living in apartment and cyberspace are considered as external factors that prevent improvement in old age. Most of the older adults have mentioned more surfing, more physical activity in their young age, and the possibility of spending more time with their families. They were also offered suggestions for a relaxed environment, love and attachment, happy life, and continuity of learning.
Acknowledgments
This research was extracted from the thesis of the second author in the Department of Education, Faculty of Education and Psychology, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lunenfeld B. The ageing male: Demographics and challenges. World Journal of Urology. 2002; 20(1):11-6. doi: 10.1007/s00345-002-0250-y
- Heravi Karimloo M, Anoosheh M, Foroughan M, Taghi Sheykhi M, Hajizade E, Seyed Bagher Maddah M, et al. [Loneliness from the perspectives of elderly people: A phenomenological study (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2008; 2(4):410-420.
- Mellor D, Russo S, McCabe MP, Davison TE, George K. Depression training program for caregivers of elderly care recipients: implementation and qualitative evaluation. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 2008; 34(9):8-15. doi: 10.3928/00989134-20080901-09
- Harrefors C, Sävenstedt S, Axelsson K. Elderly people’s perceptions of how they want to be cared for: An interview study with healthy elderly couples in Northern Sweden. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences. 2009; 23(2):353-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2008.00629.x
- Nouhi S, Karimi T, Iranmanesh S. [Comparing fear of death of the elderly settled in elderly’s home and inhabited in city houses of Isfahan (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2014; 8(4):24-31.
- Rasel M, Ardalan A. [The future of ageing and its health care costs: A warning for health system (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2007; 2(2):300-305.
- Naderi F, Roushani KH. [Relation between spiritual intelligence, social intelligence and death anxiety in Ahwaz woman senile (Persian)]. Woman and Culture. 2011; 2(6):55-67.
- Kaldi AR, Aliakbari Kamrani A, Fooroghan M. [Physical, social & mental problems of elderly in district 13 of Tehran (Persian)]. Social Welfare. 2004; 4(14):222-44.
- Tajvar M. [Elderly health and the review of their life aspects differences (Persian)]. Tehran: Nasle Farda; 2003.
- Castel AD, Balota DA, McCabe DP. Memory efficiency and the strategic control of attention at encoding: Impairments of value-directed remembering in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychology. 2009; 23(3):297-306. doi: 10.1037/a0014888
- Zhi TF, Sun XM, Li SJ, Wang QS, Cai J, Li LZ, et al. Associations of sleep duration and sleep quality with life satisfaction in elderly Chinese: The mediating role of depression. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2016; 65:211–7. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2016.03.023
- Alizadeh M, Fakhrzadeh H, Sharifi F, Zanjari N, Ghassemi S. [Comparative study of physical and mental health status of old people in aged groups of 60-64 and 65-69 years old in Tehran metropolitan area (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2013; 13(1):50-61.
- Elias SM, Neville C, Scott T. The effectiveness of group reminiscence therapy for loneliness, anxiety and depression in older adults in long-term care: A systematic review. Geriatric Nursing. 2015; 36(5):372-80. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2015.05.004
- Leszczyńska A, Daniszewska B, Pruszyńska M, Przedborska A, Hadała M, Raczkowski JW. Effects of a health improvement programme on quality of life in elderly people after falls. Polish Annals of Medicine. 2016; 23(2):129–34. doi: 10.1016/j.poamed.2016.01.008
- Vafa F, Tavakoli Rad M, Ziyadi Lotfabadi M. Dehgan M, Khodayi Gh, Salek M. [Ageing and Health (Persian)]. Mashhad: Hamsaye Aftab Publication; 2012.
- Santini ZI, Fiori KL, Feeney J, Tyrovolas S, Haro JM, Koyanagi A. Social relationships, loneliness, and mental health among older men and women in Ireland: A prospective community-based study. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2016; 204:59–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.032
- Unalan D, Gocer S, Basturk M, Baydur H, Ozturk A. Coincidence of low social support and high depressive score on quality of life in elderly. European Geriatric Medicine. 2015; 6(4):319-24. doi: 10.1016/j.eurger.2015.02.009
- Aydin R, Unal E, Gokler ME, Metintas S, Emiral GO, Ozay O, et al. An evaluation of home health care needs and Quality of Life among the elderly in a semi-rural area of Western Turkey. European Geriatric Medicine. 2016; 7(1):8-12. doi: 10.1016/j.eurger.2015.10.005
- Jing W, Willis R, Feng Z. Factors influencing quality of life of elderly people with dementia and care implications: A systematic review. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2016; 66:23-41. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2016.04.009
- Moetamedi A, Pajouhinia Sh, Fatemi Ardestani M. [The impact of spiritual wellbeing and resiliency in predicting death anxiety among elderly people in Tehran (Persian)]. Neuroscience Journal of Shefaye Khatam. 2015; 3(2):19-26.
- Nabavi SH, Shoja M, Mohammadi S, Rashedi V. [Health-related quality of life in community-dwelling older adults of Bojnourd, 2014 (Persian)]. Journal of North Khorasan University of Medical Sciences. 2014; 6(2):433-39.
- Alizadeh M, Rahimi A, Arshinji M, Sharifi F, Arzaghi M, Fakhrzadeh H. [Physical health status and socio-economic outcomes on elderly in Tehran metropolitan area (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2013; 13(1):29-37.
- Cerbone DR. Understanding phenomenology. Abingdon: Routledge; 2006.
- Todres L, Holloway I. Phenomenology. In: Cormack D, Gerrish K, Lacey A, editors. The Research Process in Nursing. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010.
- Finlay L. Debating phenomenological methods. In: Friesen N, Henriksson C, Saevi T, editors. Hermeneutic Phenomenology in Education. Berlin: Springer; 2002.
- Ghasemi H, Harirchi M, Masnavi A, Rahgozar M, Akbarian M. [Comparing quality of life between seniors living in families and institutionalized in nursing homes (Persian)]. Social Welfare. 2011; 10(39):177-200.
- Toranlu Sayadi H, Jamali R, Mir Ghafouri H. [Relationship between emotional intelligence and students’ belief in the teachings of Islam (Persian)]. Journal of Religious Thought. 2007; 3(11):145-72.
- Javadi Pashaki NJ, Mohammadi F, Jafaraghaee F, Mehrdad N. Factors influencing the successful aging of Iranian old adult women. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal. 2015; 17(7):e22451. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.22451v2
- Zanjari N, Sharifian Sani M, Hosseini Chavoshi M, Rafiey H, Mohammadi Shahboulaghi F. Perceptions of successful ageing among Iranian elders: insights from a qualitative study. The International Journal of Aging and Human Development. 2016; 83(4):381-401. doi: 10.1177/0091415016657559
- Peymanfar E, Aliakbari Dehkordi M, Mohtashami T. [A comparison between the feeling of loneliness and feeling of meaningfulness of the life of the old at the different level of religious attitudes (Persian)]. Ravanshenasi Va Din. 2012; 5(4):41-52.
- Hsu YC, Wang JJ. Physical, affective, and behavioral effects of group reminiscence on depressed institutionalized elders in Taiwan. Nursing Research. 2009; 58(4):294-9. doi: 10.1097/nnr.0b013e3181a308ee
- Nemati Dehkordi SH, Dasht Bozorgi B, Pak Seresht S, Rahekh A. [The effect of reminiscence therapy on elderly quality of life (Persian)]. Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences Journal. 2007; 9(4):75-81.
- Wang JJ, Hsu YC, Cheng SF. The effects of reminiscence in promoting mental health of Taiwanese elderly. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2005; 42(1):31-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.05.010
- Imanifar H, Bostani G, Dodman F, Raiesi R. [Facing with death from Quran and psychology viewpoints (Persian)]. Pazhoohesha-ye Miyan Reshte'e-y Quran-e Karim. 2011; 2(4):65-72.
- Habibi Sola A, Nikpour S, Sohbatzadeh R, Haghani H. [Quality of life in elderly people of west of Tehran (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Nursing Research. 2008; 2(7):29-35.
Type of Study: Research |
Subject:
gerontology
Received: 2017/06/02 | Accepted: 2017/08/15 | Published: 2018/01/01
Received: 2017/06/02 | Accepted: 2017/08/15 | Published: 2018/01/01
References
1. Lunenfeld B. The ageing male: Demographics and challenges. World Journal of Urology. 2002; 20(1):11-6. doi: 10.1007/s00345-002-0250-y [DOI:10.1007/s00345-002-0250-y]
2. Heravi Karimloo M, Anoosheh M, Foroughan M, Taghi Sheykhi M, Hajizade E, Seyed Bagher Maddah M, et al. [Loneliness from the perspectives of elderly people: A phenomenological study (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2008; 2(4):410-420.
3. Mellor D, Russo S, McCabe MP, Davison TE, George K. Depression training program for caregivers of elderly care recipients: implementation and qualita-tive evaluation. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 2008; 34(9):8-15. doi: 10.3928/00989134-20080901-09 [DOI:10.3928/00989134-20080901-09]
4. Harrefors C, Sävenstedt S, Axelsson K. Elderly people's perceptions of how they want to be cared for: An interview study with healthy elderly couples in Northern Sweden. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences. 2009; 23(2):353-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2008.00629.x [DOI:10.1111/j.1471-6712.2008.00629.x]
5. Nouhi S, Karimi T, Iranmanesh S. [Comparing fear of death of the elderly settled in elderly's home and inhabited in city houses of Isfahan (Persian)]. Irani-an Journal of Ageing. 2014; 8(4):24-31.
6. Rasel M, Ardalan A. [The future of ageing and its health care costs: A warning for health system (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2007; 2(2):300-305.
7. Naderi F, Roushani KH. [Relation between spiritual intelligence, social intelligence and death anxiety in Ahwaz woman senile (Persian)]. Woman and Cul-ture. 2011; 2(6):55-67.
8. Kaldi AR, Aliakbari Kamrani A, Fooroghan M. [Physical, social & mental problems of elderly in district 13 of Tehran (Persian)]. Social Welfare. 2004; 4(14):222-44.
9. Tajvar M. [Elderly health and the review of their life aspects differences (Persian)]. Tehran: Nasle Farda; 2003.
10. Castel AD, Balota DA, McCabe DP. Memory efficiency and the strategic control of attention at encoding: Impairments of value-directed remembering in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychology. 2009; 23(3):297-306. doi: 10.1037/a0014888 [DOI:10.1037/a0014888]
11. Zhi TF, Sun XM, Li SJ, Wang QS, Cai J, Li LZ, et al. Associations of sleep duration and sleep quality with life satisfaction in elderly Chinese: The mediat-ing role of depression. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2016; 65:211–7. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2016.03.023 [DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2016.03.023]
12. Alizadeh M, Fakhrzadeh H, Sharifi F, Zanjari N, Ghassemi S. [Comparative study of physical and mental health status of old people in aged groups of 60-64 and 65-69 years old in Tehran metropolitan area (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2013; 13(1):50-61.
13. Elias SM, Neville C, Scott T. The effectiveness of group reminiscence therapy for loneliness, anxiety and depression in older adults in long-term care: A sys-tematic review. Geriatric Nursing. 2015; 36(5):372-80. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2015.05.004 [DOI:10.1016/j.gerinurse.2015.05.004]
14. Leszczyńska A, Daniszewska B, Pruszyńska M, Przedborska A, Hadała M, Raczkowski JW. Effects of a health improvement programme on quality of life in elderly people after falls. Polish Annals of Medicine. 2016; 23(2):129–34. doi: 10.1016/j.poamed.2016.01.008 [DOI:10.1016/j.poamed.2016.01.008]
15. Vafa F, Tavakoli Rad M, Ziyadi Lotfabadi M. Dehgan M, Khodayi Gh, Salek M. [Ageing and Health (Persian)]. Mashhad: Hamsaye Aftab Publication; 2012.
16. Santini ZI, Fiori KL, Feeney J, Tyrovolas S, Haro JM, Koyanagi A. Social relationships, loneliness, and mental health among older men and women in Ire-land: A prospective community-based study. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2016; 204:59–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.032 [DOI:10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.032]
17. Unalan D, Gocer S, Basturk M, Baydur H, Ozturk A. Coincidence of low social support and high depressive score on quality of life in elderly. European Geriatric Medicine. 2015; 6(4):319-24. doi: 10.1016/j.eurger.2015.02.009 [DOI:10.1016/j.eurger.2015.02.009]
18. Aydin R, Unal E, Gokler ME, Metintas S, Emiral GO, Ozay O, et al. An evaluation of home health care needs and Quality of Life among the elderly in a semi-rural area of Western Turkey. European Geriatric Medicine. 2016; 7(1):8-12. doi: 10.1016/j.eurger.2015.10.005 [DOI:10.1016/j.eurger.2015.10.005]
19. Jing W, Willis R, Feng Z. Factors influencing quality of life of elderly people with dementia and care implications: A systematic review. Archives of Geron-tology and Geriatrics. 2016; 66:23-41. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2016.04.009 [DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2016.04.009]
20. Moetamedi A, Pajouhinia Sh, Fatemi Ardestani M. [The impact of spiritual wellbeing and resiliency in predicting death anxiety among elderly people in Tehran (Persian)]. Neuroscience Journal of Shefaye Khatam. 2015; 3(2):19-26. [DOI:10.18869/acadpub.shefa.3.2.19]
21. Nabavi SH, Shoja M, Mohammadi S, Rashedi V. [Health-related quality of life in community-dwelling older adults of Bojnourd, 2014 (Persian)]. Journal of North Khorasan University of Medical Sciences. 2014; 6(2):433-39. [DOI:10.29252/jnkums.6.2.433]
22. Alizadeh M, Rahimi A, Arshinji M, Sharifi F, Arzaghi M, Fakhrzadeh H. [Physical health status and socio-economic outcomes on elderly in Tehran metro-politan area (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2013; 13(1):29-37.
23. Cerbone DR. Understanding phenomenology. Abingdon: Routledge; 2006.
24. Todres L, Holloway I. Phenomenology. In: Cormack D, Gerrish K, Lacey A, editors. The Research Process in Nursing. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010. [PMCID]
25. Finlay L. Debating phenomenological methods. In: Friesen N, Henriksson C, Saevi T, editors. Hermeneutic Phenomenology in Education. Berlin: Springer; 2002.
26. Ghasemi H, Harirchi M, Masnavi A, Rahgozar M, Akbarian M. [Comparing quality of life between seniors living in families and institutionalized in nurs-ing homes (Persian)]. Social Welfare. 2011; 10(39):177-200.
27. Toranlu Sayadi H, Jamali R, Mir Ghafouri H. [Relationship between emotional intelligence and students' belief in the teachings of Islam (Persian)]. Journal of Religious Thought. 2007; 3(11):145-72.
28. Javadi Pashaki NJ, Mohammadi F, Jafaraghaee F, Mehrdad N. Factors influencing the successful aging of Iranian old adult women. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal. 2015; 17(7):e22451. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.22451v2 [DOI:10.5812/ircmj.22451v2]
29. Zanjari N, Sharifian Sani M, Hosseini Chavoshi M, Rafiey H, Mohammadi Shahboulaghi F. Perceptions of successful ageing among Iranian elders: insights from a qualitative study. The International Journal of Aging and Human Development. 2016; 83(4):381-401. doi: 10.1177/0091415016657559 [DOI:10.1177/0091415016657559]
30. Peymanfar E, Aliakbari Dehkordi M, Mohtashami T. [A comparison between the feeling of loneliness and feeling of meaningfulness of the life of the old at the different level of religious attitudes (Persian)]. Ravanshenasi Va Din. 2012; 5(4):41-52.
31. Hsu YC, Wang JJ. Physical, affective, and behavioral effects of group reminiscence on depressed institutionalized elders in Taiwan. Nursing Research. 2009; 58(4):294-9. doi: 10.1097/nnr.0b013e3181a308ee [DOI:10.1097/NNR.0b013e3181a308ee]
32. Nemati Dehkordi SH, Dasht Bozorgi B, Pak Seresht S, Rahekh A. [The effect of reminiscence therapy on elderly quality of life (Persian)]. Shahrekord Uni-versity of Medical Sciences Journal. 2007; 9(4):75-81.
33. Wang JJ, Hsu YC, Cheng SF. The effects of reminiscence in promoting mental health of Taiwanese elderly. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2005; 42(1):31-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.05.010 [DOI:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.05.010]
34. Imanifar H, Bostani G, Dodman F, Raiesi R. [Facing with death from Quran and psychology viewpoints (Persian)]. Pazhoohesha-ye Miyan Reshte'e-y Quran-e Karim. 2011; 2(4):65-72.
35. Habibi Sola A, Nikpour S, Sohbatzadeh R, Haghani H. [Quality of life in elderly people of west of Tehran (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Nursing Research. 2008; 2(7):29-35.
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |