Volume 16, Issue 2 (Summer 2021)
Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing 2021, 16(2): 288-303 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Mirlohi E S, Keshvari M, Mohammadi E. Effect of a Collaborative Care Training Program on Fear of Falling in the Elderly. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing 2021; 16 (2) :288-303
URL: http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-2036-en.html
URL: http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-2036-en.html
1- Department of Geriatrics and Community Health Nursing and Management, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
2- Department of Geriatrics and Community Health Nursing and Management, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. , keshvari@med.mui.ac.ir
3- Department of Nursing, School of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
2- Department of Geriatrics and Community Health Nursing and Management, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. , keshvari@med.mui.ac.ir
3- Department of Nursing, School of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
Full-Text [PDF 6980 kb]
(1914 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (3169 Views)
Full-Text: (2701 Views)
1. Introduction
Since with the improvement of health, preventive care, and living conditions, life expectancy increases and the rate of births and deaths decreases, the rate of aged population is growing. With aging, due to the gradual decline in the function of various body organs, many changes are made in the health status of the person, and thus the risk of falling, mobility limitation, and reduced daily performance increase. Falling is one of the most common problems in old age and is the result of a complex interaction between biological, economic, environmental and behavioral factors. It leads to dependency, reduced self-efficacy, depression, and reduced quality of life and imposes costs on the individual, family and society. Therefore, in designing interventions to create an active aging, special attention should be paid to its barriers including the fear of falling. Family members and caregivers should also be involved in nursing interventions and health education to reduce the fear of falling in the elderly. Various methods and programs have been used to prevent and reduce falls, but no study has been done on involving patients and their families in the implementation of interventions, decision making, and creation of preventive behaviors. The present study aims to investigate the effect of collaborative care model on fear of fall and its frequency in the elderly.
2. Materials and Methods
This is a quasi-experimental study. The study population consists of the elderly aged over 60 years covered by comprehensive health services centers in Isfahan, Iran in 2019. Using a convenience sampling method, 72 older adults (and their families) with a history of falling, adequate cognition, the presence of their caregivers or family members and not participating in other studies were selected for the study. Those who did not want to cooperate, did not attend meetings, lost consciousness, or died were excluded from the study. The intervention group participated in a collaborative care program (motivation, preparation, involvement, and evaluation) for 12 weeks, while the control group participated in two 60-minute educational sessions. Data collection was performed in three stages before, immediately and 3 months later by completing a demographic form and the Falls Efficacy Scale International (FES-I).
In the first session of intervention, explanations were given about what is the study process, how, why, by whom, where and when. In this step, an educational needs assessment was performed by examining and recognizing patients’ problems through recording history and conducting interview. This phase was lasted for 2 hours during the first week. The stages of collaborative care training program included: (a) Motivation: At this stage, the fall and its types, fear of falling and its causes, prevalence and complications were discussed with the elderly. Their attitude were different; (b) Preparation: The training group was divided into four groups of 9 for training and scheduling the training program. Participants were also explained about the nature (training and follow-up sessions), duration (45-60 minutes), and purpose of the visits; (c) Involvement: It was done with the aim of continuing the care program and involving the participants; to make sure they perform and follow up what they learned in the previous stage, to solve problems and use experiences, and to give behavior feedback to them and inform them of the extent of their participation and agreement; (d) Evaluation: The previous learning level of participants and their attitude were measured in this stage. Data were analyzed in SPSS v. 21 software using Chi-square, Mann-Whitney U, independent t-test and repeated measures ANOVA.
3. Results
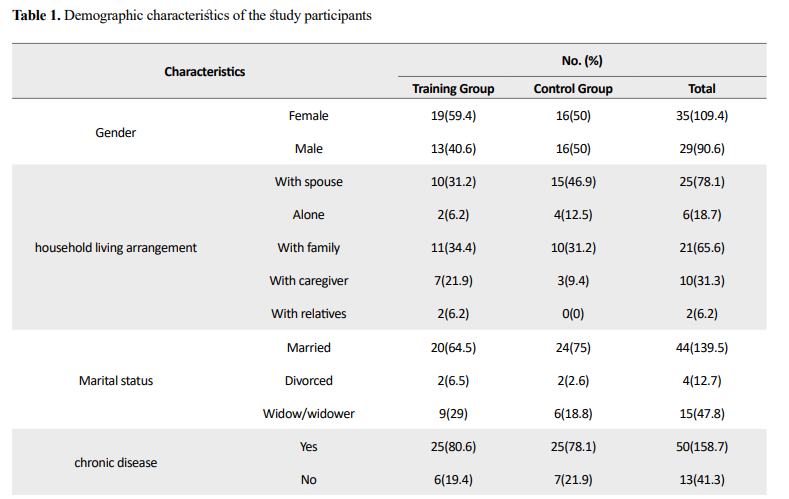
The Mean±SD age of participants was 71.34±7.47 years. The majority of them had a chronic disease, such that only 19.4% in the training group and 21.9% in the control group had no any chronic disease. Moreover, the majority of participants were taking medications such that only 22.6% in the training group and 15.6% in the control group had no medication use. Most of them in two groups had lower than high school education (84.4% in the training group). In the training group, 59.4% were women and 40.6% were men, while in the control group, 50% were women and 50% were men. Most falls in both groups occurred in different locations and were not at the same place. There was no significant difference in time of falling between the two groups. It occurred at different times (37% in the training group and 27.3% in the control group). The Mean±SD number of falls in the past 6 months was 1.59±0.24 in the training group and 1.38±0.28 in the control group. The studied groups were homogeneous in terms of the underlying factors which did not act as confounding variables (Table 1).
_s.PNG)
Independent t-test results showed that the mean scores of fear of falling before the intervention were not significantly different between the two groups (P>0.05), but immediately and 3 months after the intervention, the mean scores in the training group were significantly lower than in the control group (P<0.05). Independent t-test results showed significantly higher changes in the post-test and follow-up scores than the changes in the pretest scores in the training group compared to the control group (P<0.05).
Results of repeated measures ANOVA showed that the mean scores of fear of falling in the training group were significantly different between the three evaluation times (P<0.05). LSD post hoc test results showed that in the training group, the mean post-test score of fear of falling was significantly lower than the mean pretest score, and the mean follow-up score was lower than the mean post-test score (P<0.001). Results of repeated measures ANOVA showed that the mean scores of fear of falling were not significantly different between the three evaluation times in the control group (P>0.05). Moreover, Chi-square test results showed that the frequency of falls 3 months after the intervention in the control group was slightly higher than in the training group.
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Based on the components of collaborative care model, one of which is the involvement of patients and their families in making decisions and how to implement interventions, this study by establishing an effective, interactive and continuous relationship between team members during the care and treatment process according to the culture and family and individual conditions, collaborative care training program was provided to the elderly and lead to reduced fear of falling in them. Hence, it can be concluded that the collaborative care model reduces the fear of falls in the elderly. Therefore, it is recommended to use this simple and cost-effective program to teach patients and their families how to prevent falls and reduce the fear of falls in the elderly. Some of the limitations of the present study was the short intervention period, financial problems to solve some environmental problems, and lack of cooperation of some samples to participate in training sessions.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study obtained ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (Code: IR.MUI.RESEARCH.RES.1398.046). All ethical principles are considered in this article. The participants were informed about the purpose of the research and its implementation stages. They were also assured about the confidentiality of their information. They were free to leave the study whenever they wished, and if desired, the research results would be available to them.
Funding
This study was extracted from a Msc. thesis of first author at the Department of Geriatrics and Community Health Nursing and Management, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan.
Authors' contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing – original draft preparation: Elham Sadat Mirlohi; Writing – review & editing, visualization, supervision: All Authors; Project administration, funding acquisition: Elham Sadat Mirlohi and Mahrokh Keshvari.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Comprehensive Health Centers of Isfahan, the general physician, and the elderly who participated in the study for their cooperation.
Refrences:
Since with the improvement of health, preventive care, and living conditions, life expectancy increases and the rate of births and deaths decreases, the rate of aged population is growing. With aging, due to the gradual decline in the function of various body organs, many changes are made in the health status of the person, and thus the risk of falling, mobility limitation, and reduced daily performance increase. Falling is one of the most common problems in old age and is the result of a complex interaction between biological, economic, environmental and behavioral factors. It leads to dependency, reduced self-efficacy, depression, and reduced quality of life and imposes costs on the individual, family and society. Therefore, in designing interventions to create an active aging, special attention should be paid to its barriers including the fear of falling. Family members and caregivers should also be involved in nursing interventions and health education to reduce the fear of falling in the elderly. Various methods and programs have been used to prevent and reduce falls, but no study has been done on involving patients and their families in the implementation of interventions, decision making, and creation of preventive behaviors. The present study aims to investigate the effect of collaborative care model on fear of fall and its frequency in the elderly.
2. Materials and Methods
This is a quasi-experimental study. The study population consists of the elderly aged over 60 years covered by comprehensive health services centers in Isfahan, Iran in 2019. Using a convenience sampling method, 72 older adults (and their families) with a history of falling, adequate cognition, the presence of their caregivers or family members and not participating in other studies were selected for the study. Those who did not want to cooperate, did not attend meetings, lost consciousness, or died were excluded from the study. The intervention group participated in a collaborative care program (motivation, preparation, involvement, and evaluation) for 12 weeks, while the control group participated in two 60-minute educational sessions. Data collection was performed in three stages before, immediately and 3 months later by completing a demographic form and the Falls Efficacy Scale International (FES-I).
In the first session of intervention, explanations were given about what is the study process, how, why, by whom, where and when. In this step, an educational needs assessment was performed by examining and recognizing patients’ problems through recording history and conducting interview. This phase was lasted for 2 hours during the first week. The stages of collaborative care training program included: (a) Motivation: At this stage, the fall and its types, fear of falling and its causes, prevalence and complications were discussed with the elderly. Their attitude were different; (b) Preparation: The training group was divided into four groups of 9 for training and scheduling the training program. Participants were also explained about the nature (training and follow-up sessions), duration (45-60 minutes), and purpose of the visits; (c) Involvement: It was done with the aim of continuing the care program and involving the participants; to make sure they perform and follow up what they learned in the previous stage, to solve problems and use experiences, and to give behavior feedback to them and inform them of the extent of their participation and agreement; (d) Evaluation: The previous learning level of participants and their attitude were measured in this stage. Data were analyzed in SPSS v. 21 software using Chi-square, Mann-Whitney U, independent t-test and repeated measures ANOVA.
3. Results
The Mean±SD age of participants was 71.34±7.47 years. The majority of them had a chronic disease, such that only 19.4% in the training group and 21.9% in the control group had no any chronic disease. Moreover, the majority of participants were taking medications such that only 22.6% in the training group and 15.6% in the control group had no medication use. Most of them in two groups had lower than high school education (84.4% in the training group). In the training group, 59.4% were women and 40.6% were men, while in the control group, 50% were women and 50% were men. Most falls in both groups occurred in different locations and were not at the same place. There was no significant difference in time of falling between the two groups. It occurred at different times (37% in the training group and 27.3% in the control group). The Mean±SD number of falls in the past 6 months was 1.59±0.24 in the training group and 1.38±0.28 in the control group. The studied groups were homogeneous in terms of the underlying factors which did not act as confounding variables (Table 1).

_s.PNG)
Independent t-test results showed that the mean scores of fear of falling before the intervention were not significantly different between the two groups (P>0.05), but immediately and 3 months after the intervention, the mean scores in the training group were significantly lower than in the control group (P<0.05). Independent t-test results showed significantly higher changes in the post-test and follow-up scores than the changes in the pretest scores in the training group compared to the control group (P<0.05).
Results of repeated measures ANOVA showed that the mean scores of fear of falling in the training group were significantly different between the three evaluation times (P<0.05). LSD post hoc test results showed that in the training group, the mean post-test score of fear of falling was significantly lower than the mean pretest score, and the mean follow-up score was lower than the mean post-test score (P<0.001). Results of repeated measures ANOVA showed that the mean scores of fear of falling were not significantly different between the three evaluation times in the control group (P>0.05). Moreover, Chi-square test results showed that the frequency of falls 3 months after the intervention in the control group was slightly higher than in the training group.
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Based on the components of collaborative care model, one of which is the involvement of patients and their families in making decisions and how to implement interventions, this study by establishing an effective, interactive and continuous relationship between team members during the care and treatment process according to the culture and family and individual conditions, collaborative care training program was provided to the elderly and lead to reduced fear of falling in them. Hence, it can be concluded that the collaborative care model reduces the fear of falls in the elderly. Therefore, it is recommended to use this simple and cost-effective program to teach patients and their families how to prevent falls and reduce the fear of falls in the elderly. Some of the limitations of the present study was the short intervention period, financial problems to solve some environmental problems, and lack of cooperation of some samples to participate in training sessions.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study obtained ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (Code: IR.MUI.RESEARCH.RES.1398.046). All ethical principles are considered in this article. The participants were informed about the purpose of the research and its implementation stages. They were also assured about the confidentiality of their information. They were free to leave the study whenever they wished, and if desired, the research results would be available to them.
Funding
This study was extracted from a Msc. thesis of first author at the Department of Geriatrics and Community Health Nursing and Management, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan.
Authors' contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing – original draft preparation: Elham Sadat Mirlohi; Writing – review & editing, visualization, supervision: All Authors; Project administration, funding acquisition: Elham Sadat Mirlohi and Mahrokh Keshvari.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Comprehensive Health Centers of Isfahan, the general physician, and the elderly who participated in the study for their cooperation.
Refrences:
- World Health Organization. WHO global report on falls prevention in older age [Internet]. 2008 [Updated 2008]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43811
- World Health Organization. World report on ageing and health [Internet]. 2015 [Updated 2015]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/186463
- Williams PA. Basic geriatric nursing. 6th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2016. https://books.google.se/books?id=YAzhCgAAQBAJ&dq
- Meiner SE, Meiner S. Gerontologic nursing. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2015. https://books.google.com/books/about/Gerontologic_Nursing.html?id=2TDdoAEACAAJ
- Ungar A, Rafanelli M, Iacomelli I, Brunetti MA, Ceccofiglio A, Tesi F, et al. Fall prevention in the elderly. Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism. 2013; 10(2):91-5. [PMID] [PMCID]
- Najafi Ghezeljeh T, Parsa Yekta Z, Mehran A, Jafari Oori M. [Effect of a multidimensional fall prevention program on incidence of falling and quality of life among elderly (Persian)]. Hayat Journal. 2014; 20(2):14-24. http://hayat.tums.ac.ir/article-1-787-en.html
- Nabavi SH, Hatami ST, Norouzi F, Gerivani Z, Hatami SE, Monadi Ziarat H, et al. [Prevalence of fall and its related factors among older people in Bojnurd in 2015 (Persian)]. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing . 2016; 11(3):466-73. [DOI:10.21859/sija-1103466]
- Taheri Tanjani P, Ainy E, Akbarpuor S, Soori H. [Study of characteristics of falls among Iranian elders (Persian)]. IIrtiqā-yi Īminī va Pīshgīrī az Masdūmiyat/ha. 2015; 2(4):313-20. [DOI:10.22037/meipm.v2i4.8398]
- Abbasi M, Daniali SSM, Hazrati M. [Lifestyle of fallen elderly patients referred to Isfahan hospitals (Persian)]. Iran Journal of Nursing. 2017; 30(107):20-31. [DOI:10.29252/ijn.30.107.20]
- Scheffer AC, Schuurmans MJ, van Dijk N, van der Hooft T, de Rooji SE. Fear of falling: Measurement strategy, prevalence, risk factors and consequences among older persons. Age and Aging. 2008; 37(1):19-24. [DOI:10.1093/ageing/afm169]
- Jafarian Amiri SR, Zabihi A, Aziznejad Roshan P, Hosseini SR, Bijani A. [Fall at home and its related factors among the elderly in Babol city Iran (Persian)]. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences. 2013; 15(5):95-101. http://jbums.org/article-1-4527-en.html
- Orces CH. Prevalence and determinants of fall-related injuries among older adults in Ecuador. Current Gerontology and Geriatrics Research. 2014; 2014:863473. [DOI:10.1155/2014/863473]
- Buttaro TM, Aznavorian S, Dick K. Clinical management of patients in subacute and long-term care settings. Amsterdam: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2006. https://books.google.com/books?hl
- Jalalvandi F, Esmaeilivand M, Safari Faramani R. [Assessing frequency of trauma among elderly attending to Taleghani Hospital in Kermanshah during the first six months of 2008 (Persian)]. Journal of Geriatric Nursing. 2015; 1(3):47-54. http://jgn.medilam.ac.ir/article-1-101-en.html
- Tabloski PA. Gerontological nursing. London: Pearson Education; 2013. https://books.google.com/books?id=hd0vAAAAQBAJ&dq
- Legters K. Fear of falling. Physical Therapy. 2002; 82(3):264-72. [DOI:10.1093/ptj/82.3.264]
- Tinetti ME, Richman D, Powell L. Falls efficacy as a measure of fear of falling. Journal of Gerontology. 1990; 45(6):239-43. [DOI:10.1093/geronj/45.6.p239]
- Miller CA, Hunter S. Miller's nursing for wellness in older adults. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012.
- Azadi F, Mohammadi E. [Effects of partnership care model on quality of life (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Nursing Research. 2006; 1(2):23-9. http://ijnr.ir/article-1-28-fa.html
- Rezapour P, Shahriari M, Moieni M, Sanei H. Investigating the effect of collaborative care on depression, anxiety, and stress of patients after coronary angioplasty. Medical - Surgical Nursing Journal. 2016; 5 (2):e68014. https://sites.kowsarpub.com/msnj/articles/68014.html
- Mamene M, Lakdizaji S, Rahmani A, Behshid M. [The effect of education based on the collaborative care model on the nutritional behaviors of family members of patients with type II diabetes (Persian)]. Medical - Surgical Nursing Journal. 2014; 3(2):e87910. https://sites.kowsarpub.com/msnj/articles/87910.html
- Von Korff M, Katon WJ, Lin EH, Ciechanowski P, Peterson D, Ludman EJ, et al. Functional outcomes of multi-condition collaborative care and successful ageing: Results of randomised trial. BMJ. 2011; 343:d6612. [DOI:10.1136/bmj.d6612]
- Mozaffari N, Mohammadi MA, Samadzadeh S. [Effect of fall care behaviors training on fear of falling among the elderly people referred to health centers: A double-blind randomized clinical trial (Persian)]. Hayat Journal. 2018; 24(3):220-32. http://hayat.tums.ac.ir/article-1-2496-en.html
- Tennstedt Sh, Howland J, Lachman M, Peterson E, Kasten L, Jette A. A randomized, controlled trial of a group intervention to reduce fear of falling and associated activity restriction in older adults. The Journals of Gerontology: Series B. 1998; 53B(6):384-92. [DOI:10.1093/geronb/53b.6.p384]
- Brouwer BJ, Walker C, Rydahl SJ, Culham EG. Reducing fear of falling in seniors through education and activity programs: A randomized trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2003; 51(6):829-34. [DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.51265.x]
- Salminen MJ, Vahlberg TJ, Salonoja MT, Aarnio PTT, Kivelä SL. Effect of a risk-based multifactorial fall prevention program on the incidence of falls. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2009; 57(4):612-9. [DOI:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02176.x]
- Hornyak V, Brach JS, Wert DM, Hile E, Studenski S, Van Swearingen JM. What is the relation between fear of falling and physical activity in older adults? Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2013; 94(12):2529-34. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2013.06.013]
- Lim JY, Jang SN, Park WB, Oh MK, Kang EK, Paik NJ. Association between exercise and fear of falling in community-dwelling elderly Koreans: Results of a cross-sectional public opinion survey. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2011; 92(6):954-9. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2010.12.041]
- Schmid AA, van Puymbroeck M, Koceja DM. Effect of a 12-week yoga intervention on fear of falling and balance in older adults: A pilot study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2010; 91(4):576-83. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2009.12.018]
- Gawler S, Skelton DA, Dinan-Young S, Masud T, Morris RW, Griffin M, et al. Reducing falls among older people in general practice: The ProAct65+ exercise intervention trial. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2016; 67:46-54. [DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2016.06.019]
- Avineri E, Shinar D, Susilo YO. Pedestrians’ behaviour in cross walks: The effects of fear of falling and age. Accident Analysis & Prevention. 2012; 44(1):30-4. [DOI:10.1016/j.aap.2010.11.028]
- Ghotbi N, Seyed Bagher Maddah S, Dalvandi A, Arsalani N, Farzi M. [The effect of education of self care behaviors based on family-centered empowerment model in type II diabetes (Persian)].Advances in Nursing & Midwifery. 2014; 23(83):35-42. https://journals.sbmu.ac.ir/en-jnm/article/view/7027
- Ellis SE, Speroff T, Dittus RS, Brown A, Pichert JW, Elasy TA. Diabetes patient education: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Patient Education and Counseling. 2004; 52(1):97-105. [DOI:10.1016/S0738-3991(03)00016-8]
- Rabie Siahkali S, Pourmemari MH, Khaleghdoost Mohammadi T, Askandari F, Avazeh A. [Study on effective factors on patients’ family members anxiety in intensive care units (Persian)]. Journal of Advances in Medical and Biomedical Research. 2010; 18(70):91-101. http://zums.ac.ir/journal/article-1-1088-en.html
- Sanaie N, Nejati S, Zolfaghari M, Alhani F, KazemNejad A. [The effect of family-centered empowerment in self efficacy and self esteem in patients undergoing coronary bypass graft surgery (Persian)]. Journal of Research Development in Nursing & Midwifery. 2013; 10(2):44-53. http://nmj.goums.ac.ir/article-1-455-en.pdf
- Khajavi D. [Validation and reliability of Persian version of Fall Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I) in community-dwelling older adults (Persian)]. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2013; 8(2):39-47. http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-602-en.html
- Azadi A, Bastami M, Mmalek M, Nikbakht Nasr Abadi AR, Bastami AR, Pashaii Sabet F. [Effect of fall-preventive program on fear of falling, falling frequency, and quality of life in the elderly living in nursing homes (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Nursing Research. 2017; 12(4):68-75. [DOI:10.21859/ijnr-12049]
- Yardley L, Smith H. A prospective study of the relationship between feared consequences of falling and avoidance of activity in community-living older people. The Gerontologist. 2002; 42(1):17-23. [DOI:10.1093/geront/42.1.17]
- Howland J, Peterson EW, Levin WC, Fried L, Pordon D, Bak Sh. Fear of falling among the community-dwelling elderly. Journal of Aging and Health. 1993; 5(2):229-43. [DOI:10.1177/089826439300500205]
- Parvareshan S, Shamsalinia A, Jahanshahi M, Hajiahmadi M. [Impact of family-based empowering model on the perceived threat and self-efficacy of families of diabetic elderly at risk of falling (Persian)]. Journal of Clinical Nursing and Midwifery. 2018; 7(2):96-107. http://jcnm.skums.ac.ir/article-1-775-en.html
- Wetherell JL, Petkus AJ, Thorp SR, Stein MB, Chavira DA, Campbell-Sills L, et al. Age differences in treatment response to a collaborative care intervention for anxiety disorders. The British Journal of Psychiatry. 2013; 203(1):65-72. [DOI:10.1192/bjp.bp.112.118547]
- Borji M, Motaghi M. [The effect of collaborative care model on social support and general self-efficacy of the elderly (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Psychiatric Nursing. 2017; 5(1):22-9. [DOI:10.21859/ijpn-05014]
- Beach SR, Walker J, Celano CM, Mastromauro CA, Sharpe M, Huffman JC. Implementing collaborative care programs for psychiatric disorders in medical settings: A practical guide. General Hospital Psychiatry. 2015; 37(6):522-7. [DOI:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2015.06.015]
- Najafi Ghezlcheh T, Ariapour S, Jafari Oori M. [Epidemiology and relationship of fall and fear of falling in the elderly residing at Kamrani nursing home, Tehran, Iran (Persian)]. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2016; 10(4):152-61. http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-791-en.html
- Taheri M, Mirmoezzi M, Sabaghi MF. [Effects of aquatic on balance and preventing of fall among healthy elderly men (Persian)]. Irtiqā-yi Īminī va Pīshgīrī az Masdūmiyat/ha. 2019; 6(3):144-51. [DOI:10.22037/meipm.v6i3.23993]
- Rezaei Evrigh M, Mohamadi F, Azimian J, Motalebi SA. [The effect of a simple balance training program on fall prevention in the elderly women hospitalized in razi psychiatric hospital, Tehran (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Rehabilitation Research in Nursing. 2017; 3(4):43-9. [DOI:10.21859/ijrn-03046]
- Farhad L, Brazparandjani Sh, Latifi SM, Chahkhoei M, Khalili A, Paymard A, et al. [The effect of collaborative care model on the fatigue in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: A randomized clinical trial (Persian)]. Qom University of Medical Sciences Journal. 2016; 10(8):71-9. http://journal.muq.ac.ir/article-1-544-en.html
- Nayyeri S, Golafrooz M, Sadeghi H, Amini S, Zarrabi L, Rakhshani MH. [The effect of the partnership care model on the quality of sleep among patients with heart failure (Persian)]. Journal of Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences. 2015; 22(2):289-99. http://jsums.medsab.ac.ir/article_563.html
- Lashkari F, Shariati A, Baraz Sh, Latifi M. Collaborative care model effect on the patients’ sleep quality with maintenance hemodialysis. Jundishapur Journal of Chronic Disease Care. 2013; 2(1-2):1-7. https://sites.kowsarpub.com/jjcdc/articles/76762.html
- Shokati Ahmadabad M. [The effect of collaborative care model on quality of life in stroke patients Neurology Research Center of Iran in 2007 (Persian)]. [PhD. dissertation]. Tehran: Tehran University of Medical Sciences. https://ganj.irandoc.ac.ir/#/search?keywords=
Type of Study: Research |
Subject:
nursing
Received: 2020/06/09 | Accepted: 2020/12/02 | Published: 2021/07/13
Received: 2020/06/09 | Accepted: 2020/12/02 | Published: 2021/07/13
References
1. 1) World Health Organization, World Health Organization. Ageing, Life Course Unit. WHO global report on falls prevention in older age. World Health Organization;2008, Available at: URLE: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43811
2. 2) World Health Organization. World report on ageing and health. World Health Organization; 2015 Oct 22, Available at: URLE: https://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2015/older-persons-day/en/
3. 3) Williams P, 2016," Basic Geriatric Nursing", 6TH Edition.
4. 4) Meiner.Sue E, 2015, "Gerontologic Nursing" 15TH Edition.
5. 5) Ungar A, Rafanelli M, Iacomelli I, Brunetti MA, Ceccofiglio A, Tesi F, Marchionni N. Fall prevention in the elderly. Clinical Cases in mineral and bone metabolism. 2013 May;10(2):91, Available at: URLE. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24133524
6. 6) Najafi Ghezeljeh T, Parsa Yekta Z, Mehran A, Jafari Oori M. Effect of a Multidimensional Fall Prevention Program on Incidence of Falling and Quality of Life among Elderly. Hayat.2014; 20 (2):14-24. (Persian) http://www.nmsjournal.com/text.asp?2019/8/2/78/257441
7. 7) Nabavi SH, Hatami ST, Norouzi F, Gerivani Z, Hatami SE, Monadi Ziarat H, Delbari A. Prevalence of fall and its related factors among older people in bojnurd in 2015. Iranian JournalofAgeing.2016Oct15;11(3):46673.(Persian).http://dx.doi.org/10.21859/sija110346 [DOI:10.21859/sija-1103466]
8. 8) Tanjani PT, Ainy E, Akbarpuor S, Soori H. Study of characteristics of falls among Iranian elders. Safety Promotion and Injury Prevention. 2015 ;2(4):313-20. (Persian). http://journals.sbmu.ac.ir/en-spip/issue/view/806
9. 9) Abbasi M, Daniali SS, Hazrati M. Lifestyle of fallen elderly patients referred to Isfahan hospitals. Iran Journal of Nursing. 2017 Aug;30(107):20-31. (Persian). http://dx.doi.org/10.29252/ijn.30.107.20 [DOI:10.29252/ijn.30.107.20]
10. 10) Scheffer, A.Schuurmans, M. Dijk, N. Hooft, T. Rooji, S .2008. " Fear of falling: measurement strategy, prevalence, risk factors and consequences among older persons". Age and Aging.Vol:37. Pp:19-24. , Available at: URLE [DOI:10.1093/ageing/afm169]
11. 11) Jafarian Amiri S, Zabihi A, Aziznejad Roshan P, Hosseini S, Bijani A. Fall at Home and its Related Factors among the Elderly in Babol City Iran. JBUMS.2013; 15 (5) :95-101. [Persian] , Available at: URLE http://jbums.org/article-1-4527-en.html
12. 12) Orces CH. Prevalence and determinants of fall-related injuries among older adults in Ecuador. Current gerontology and geriatrics research. 2014;2014. , Available at: URLE [DOI:10.1155/2014/863473]
13. 13) Buttaro, T, M, Trybulski, J, Bailery, P, P & Sandberg- Cook, J, 2006, "Clinical Management of Patients in Subacute and Long-Term Care Settings"2 TH Edition.
14. 14) Jalalvandi F, Esmaeilivand M, Safari Faramani R. Assessing frequency of trauma among elderly attending to Taleghani Hospital in Kermanshah during the first six months of2008. jgn. 2015; 1 (3) :47-54. (Persian). http://jgn.medilam.ac.ir/article-1-101-en.html
15. 15) Tabloski PA. Gerontological nursing. Pearson Higher Ed; 2013 May24
16. 16) Letters K. Fear of falling. Physical therapy.2002 Mar,1;82(3):264-72. [DOI:10.1093/ptj/82.3.264]
17. 17) Tinetti ME, Richman D, Powell L. Falls efficacy as a measure of fear of falling. Journal of gerontology. 1990 Nov 1;45(6): P239-43. , Available at: URLE
https://doi.org/10.1093/geronj/45.6.P239 [DOI:10.1093/geronj/45.6.p239]
18. 18) Miller CA. Nursing for wellness in older adults 6th ed. United of State America, Lippincort William and Wilkins. 2012.
19. 19) Azadi F, Mohammadi E. Effects of Partnership Care Model on quality of life. Iranian Journal of Nursing Research. 2006 Nov 10;1(2):0, [Persian].Available at: URLE http://ijnr.ir/article-1-28-en.html
20. 20) Rezapour P, Shahriari M, Moieni M, Sanei H, Evaluation of the effect of collaborative care on depression, anxiety and stress of patients after coronary angioplasty, Iranian Journal of Medical - Surgical Nursing, 2016; 5(2): 59-66. magiran.com/p1592141. [Persian]. Available at: URLE: https://www.magiran.com/volume/111338
21. 21) MAMENE M, LAKDIZAJI S, RAHMANI A, BEHSHID M. The effect of education based on the collaborative care model on the nutritional behaviors of family members of patients with type II diabetes. [Persian]. Available at: URLE; https://www.sid.ir/en/journal/JournalListPaper.aspx?ID=2024623
22. 22) Von Korff M, Katon WJ, Lin EH, Ciechanowski P, Peterson D, Ludman EJ, Young B, Rutter CM. Functional outcomes of multi-condition collaborative care and successful ageing: results of randomised trial. Bmj. 2011 Nov 10;343: d6612. https://dx.doi.org/10.1136%2Fbmj.d6612 [DOI:10.1136/bmj.d6612]
23. 23) Mozaffari N, Mohammadi M A, Samadzadeh S. Effect of fall care behaviors training on fear of falling among the elderly people referred to health centers: A double-blind randomized clinical trial Hayat. 2018; 24 (3) :220-232URL: http://hayat.tums.ac.ir/article1-2496-fa.html.
24. 24) Tennstedt S, Howland J, Lachman M, Peterson E, Kasten L, Jette A. A randomized, controlled trial of a group intervention to reduce fear of falling and associated activity restriction in older adults. The Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences. 1998 Nov1;53(6): P384-92.
https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/53B.6.P384 [DOI:10.1093/geronb/53b.6.p384]
25. 25) Brouwer BJ, Walker C, Rydahl SJ, Culham EG. Reducing fear of falling in seniors through education and activity programs: a randomized trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2003 Jun;51(6):829-34. [DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.51265.x]
26. 26) Salminen MJ, Vahlberg TJ, Salonoja MT, Aarnio PT, Kivelä SL. Effect of a risk‐based multifactorial fall prevention program on the incidence of falls. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2009 Apr;57(4):612-9.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02176.x [DOI:10.1111/j.15325415.2009.02176.x]
27. 27) Hornyak V, Brach JS, Wert DM, Hile E, Studenski S, Van Swearingen JM. What is the relation between fear of falling and physical activity in older adults? Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2013 Dec1;94(12):2529-34. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2013.06.013]
28. 28) Lim JY, Jang SN, Park WB, Oh MK, Kang EK, Paik NJ. Association between exercise and fear of falling in community-dwelling elderly Koreans: Results of a cross-sectional public opinion survey. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2011 Jun 1;92(6):954-9. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2010.12.041]
29. 29) Schmid AA, Van Puymbroeck M, Koceja DM. Effect of a 12-week yoga intervention on fear of falling and balance in older adults: a pilot study. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation.2010 Apr 1;91(4):576-83. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2009.12.018]
30. 30) Gawler S, Skelton DA, Dinan-Young S, Masud T, Morris RW, Griffin M, Kendrick D, Iliffe S. Reducing falls among older people in general practice: The ProAct65+ exercise intervention trial. Archives of gerontology and geriatrics. 2016 Nov 1; 67:46-54. [DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2016.06.019]
31. 31) Avineri E, Shinar D, Susilo YO. Pedestrians' behaviour in cross walks: the effects of fear of falling and age. Accident Analysis & Prevention. 2012 Jan1;44(1):30-4. [DOI:10.1016/j.aap.2010.11.028]
32. 32) Ghotbi N, Maddah SB, Dalvandi A, Arsalani N, Farzi M. The effect of education of self care behaviors based on family-centered empowerment model in type II diabetes (Persian). J Nurs Midwifery Fac Shahid Beheshti Univ Med Sci. 2014; 23(83):43-50.
33. 33) Ellis SE, Speroff T, Dittus RS, Brown A, Pichert JW, Elasy TA. Diabetes patient education: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Patient Educ Couns. 2004; 52(1):97-105. [DOI:10.1016/S0738-3991(03)00016-8]
34. 34) Rabie Siahkali S, Pourmemari M, Khaleghdoost Mohammadi T, Askandari F, Avazeh A. Study on effective factors on patients' family members anxiety in intensive care units (Persian). J Zanjan Univ MedSci. 2010; 18(70):91-101.
35. 35) Sanaye N. Impact of family-centered empowerment on self-efficacy and self-esteem of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (Persian) [Master thesis]. Zanjan: Zanjan University of Medical Sciences;2011.
36. 36) Khajavi D. Validation and Reliability of Persian Version of Fall Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I) in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing.2013;8(2):39.47 [Persian] http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-602-fa.html
37. 37) Azadi A, Bastami M, Mmalek M. Effect of Fall-Preventive Program on Fear of Falling, Falling Frequency, and Quality of Life in the Elderly Living in Nursing Homes. Iranian Journal of Nursing Research. 2017 Oct10;12(4):68,75. [Persian]. http://dx.doi.org/10.21859/ijnr-12049 [DOI:10.21859/ijnr-12049]
38. 38) Yardley L, Smith H. A prospective study of the relationship between feared consequences of falling and avoidance of activity in community-living older people. The Gerontologist.2002 Feb1;42(1):17-23. [DOI:10.1093/geront/42.1.17]
39. 39) Howland J, Peterson EW, Levin WC, Fried L, Pordon D, Bak S. Fear of falling among the community-dwelling elderly. Journal of aging and health. 1993 May;5(2):229-43. [DOI:10.1177/089826439300500205]
40. 40) Parvareshan S, Shamsalinia A, Jahanshahi M, Hajiahmadi M. Impact of Family-Based Empowering Model on the Per-ceived Threat and Self-Efficacy of Families of Diabetic Elderly at Risk of Falling. Journal of Clinical Nursing and Midwifery. 2018;7(2):96-107.
41. 41) Wetherell JL, Petkus AJ, Thorp SR, Stein MB, Chavira DA, Campbell-Sills L, Craske MG, Sherbourne C, Bystritsky A, Sullivan G, Roy-Byrne P. Age differences in treatment response to a collaborative care intervention for anxiety disorders. The British Journal of Psychiatry. 2013 Jul;203(1):65-72. https://dx.doi.org/10.1192%2Fbjp.bp.112.118547. [DOI:10.1192/bjp.bp.112.118547]
42. 42) Borji M, Motaghi M. The Effect of Collaborative Care Model on Social Support and General Self-Efficacy of the Elderly. Iranian Journal of Psychiatric Nursing. 2017 May 10;5(1):22-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.21859/ijpn-05014 [DOI:10.21859/ijpn-05014]
43. 43) Beach SR, Walker J, Celano CM, Mastromauro CA, Sharpe M, Huffman JC. Implementing collaborative care programs for psychiatric disorders in medical settings: a practical guide. General hospital psychiatry. 2015 Nov 1;37(6):522-7. [DOI:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2015.06.015]
44. 44) Najafi Ghezlcheh T, Ariapour S, Jafari Oori M. Epidemiology and relationship of fall and fear of falling in the elderly residing at Kamrani nursing home, Tehran, Iran. Iranian Journal of Ageing.2016 Jan10;10(4):15261. [Persian]. http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-791-en.html.
45. 45) Taheri M, Mirmoezzi M, Sabaghi M. Effects of aquatic on balance and preventing of fall among healthy elderly men. J. Saf. Promot. Inj. Prev. 2018 Jan 1; 6:144-51. http://journals.sbmu.ac.ir/en-spip/issue/view/1758
46. 46) Eyvarigh MR, Mohammadi F, Azimian J, Motallebi SA. The effect of a simple balance training program on fall prevention in the elderly women hospitalized in razi psychiatric hospital, Tehran. Iranian Journal of Rehabilitation Research in Nursing. 2017;3(4):42-8. http://ijrn.ir/article-1-241-fa.html [DOI:10.21859/ijrn-03046]
47. 47) Farhad L, Brazparandjani S, Latifi SM, Chahkhoei M, Khalili A, Paymard A, Dehghani F, Shariati A. The effect of collaborative care model on the fatigue in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: A randomized clinical trial. Qom University of Medical Sciences Journal. 2016 Nov 10;10(8):71-9.
48. 48) Nayyeri S, Golafrooz M, Sadaghi H, Amini S, Zarrabi L, Rakhshani M. The effect of the partnership care model on the quality of sleep among patients with heart failure. Quarterly Journal of Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences. 2015;22(2):289-99. http://dx.doi.org/10.29252/mcs.4.1.39 [DOI:10.29252/mcs.4.1.39]
49. 49) Lashkari F, Shariati B, Baraz Sh, Latifi M. Collaborative care model effect on the patients' sleep quality with maintenance hemodialysis. Jundishapur J Chronic Dis Care 2013:2(2):45-9.
50. 50) Shokati Ahmadabad M. The effect of collaborative care model on quality of life in stroke patients Neurology Research Center of Iran in 2007 (Doctoral dissertation, MSc Thesis]. Tehran: Tehran University of Medical Sciences).
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |








