Volume 14, Issue 1 (Spring 2019)
Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing 2019, 14(1): 2-13 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Taheri M, Irandoust K. The Effect of Omega-3 Supplementation and Functional Exercises on the Psychomotor Performance of Aged Women in Qazvin. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing 2019; 14 (1) :2-13
URL: http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-1552-en.html
URL: http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-1552-en.html
1- Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, Faculty of Social Sciences, Imam Khomeini International University, Qazvin, Iran. , taheri_morteza@yahoo.com
2- Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, Faculty of Social Sciences, Imam Khomeini International University, Qazvin, Iran.
2- Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, Faculty of Social Sciences, Imam Khomeini International University, Qazvin, Iran.
Full-Text [PDF 2143 kb]
(3005 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (7262 Views)
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the International University of Imam Khomeini with the code of 17628.
Funding
This research has been extracted from the research project (No. 11821) funded by Imam Khomeini International University.
Authors contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: Morteza Taheri; Editing and Finalization: Khadijeh Irandoust.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Full-Text: (3863 Views)
Extended Abstract
1. Objectives
n a 100-year interval, the number of elderly people aged ≥60 years has been tripled. Furthermore, it is estimated that the aged population will increase from 11% of the total world population in 1950 to 30% of that by 2050 [1]. Changes occurring in various body systems cause mobility limitations in aged people and impair their functional independence [2]. Evidence suggests abnormalities in the psychomotor performance of the elderly, which may lead to more impaired functional independence. One of these effective indicators is the information processing ability that includes factors such as reaction time, attention capacity, and ability to respond to environmental stimuli [4]. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of omega-3 supplementation and functional exercises on the psychomotor performance of aged women.
2. Methods and Materials
This was a quasi-experimental study with Pre-test-Post-test design conducted in 2017 on 47 elderly women aged 60-70 years. The study participants were recruited from the Sports and Health Consultation Center of Qazvin Sports and Youth Department based on convenience sampling method. They were randomly assigned to 4 groups of functional exercises (EX), omega-3 supplementation (SUP), exercise+omega-3 supplementation (EX+SUP), and placebo. Inclusion criteria were the age of ≥60 years, not susceptible to omega-3 or fish supplements’ adverse effects, the ability to participate in training exercises, and no mobility limitations. To assess the readiness of subjects during training, the Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire (PAR-Q) was used.
The nutritional analysis of study subjects was examined before testing by N4 software to control the effect of nutrition on the results. The two groups of SUP and EX+SUP received two 2000 mg of omega-3 capsules (EPA 180 and DHA 120, Zahrawi Co.) daily for 8 weeks in the morning and night. The placebo group received two capsules containing 2% dextrose solution (Zakaria Co.). The functional exercise protocol was designed according to the American College of Sports Medicine instructions, consisting of 3 sessions/week (Saturday, Monday and Wednesday) for 50 min from 10:00 AM to 11:30 AM, and at least 1 hour after breakfast. Each session included a 10-min warm up, a 45-min strength and endurance training, and a 5-min cool down [5].
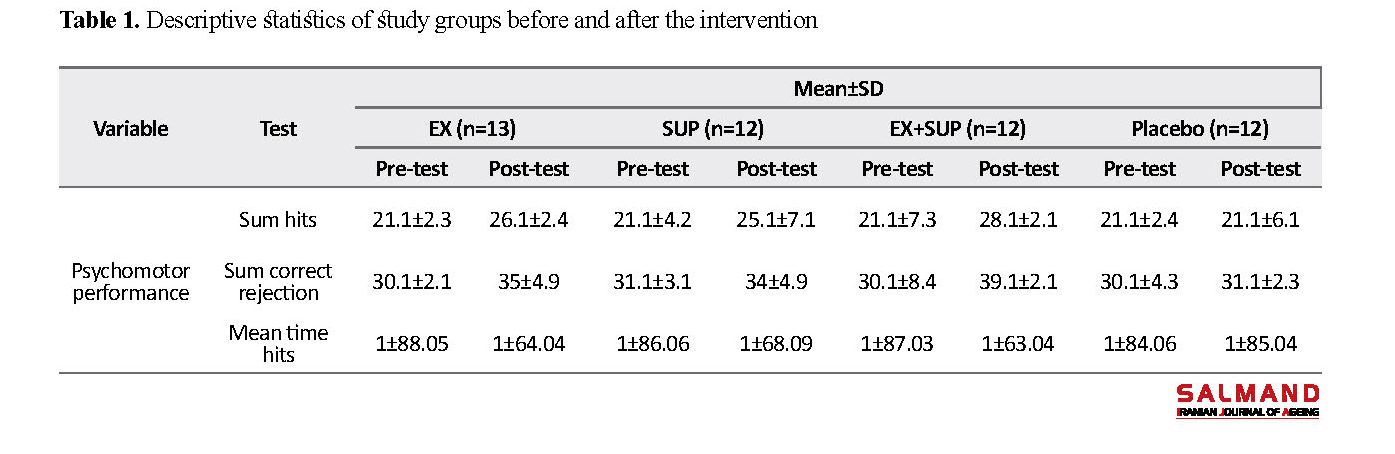
Psychomotor performance was measured using the Vienna test system which has acceptable validity. One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Multivariate Analysis of Covariance (MANCOVA) were used for analyzing the collected data. Descriptive statistics of study groups before and after the intervention are presented in Table 1.
3. Results
The Smirnov-Kolmogorov test results suggested the normal distribution of the obtained data (P>0.05). One-way ANOVA used for comparing the nutritional status of subjects reported no significant difference on the day before the pre-test phase (P>0.05). Groups EX, SUP, and EX-SUP demonstrated significant improvements in all psychomotor tests (P<0.05). By performing repeated measures ANOVA on three components in the 4 groups, a significant difference between the mean Pre-test and Post-test scores was observed (P<0.05). By removing the Pre-test effect, it was revealed that when a combination of omega-3 supplementation and functional exercises was used, the best results were achieved and their psychomotor performance was improved.
4. Conclusion
Any exercise intervention addressing aged people with mental challenges in terms of information processing and leading them to the problem-solving process can enhance their psychomotor performance. Based on the obtained results, the study participants’ response and precision of functional performance improved after exercise and supplementation interventions; this finding is very important in the motor control of aged people. This study reported improved psychomotor performance following functional exercising and omega-3 supplementation which should be considered by policymakers.
1. Objectives
n a 100-year interval, the number of elderly people aged ≥60 years has been tripled. Furthermore, it is estimated that the aged population will increase from 11% of the total world population in 1950 to 30% of that by 2050 [1]. Changes occurring in various body systems cause mobility limitations in aged people and impair their functional independence [2]. Evidence suggests abnormalities in the psychomotor performance of the elderly, which may lead to more impaired functional independence. One of these effective indicators is the information processing ability that includes factors such as reaction time, attention capacity, and ability to respond to environmental stimuli [4]. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of omega-3 supplementation and functional exercises on the psychomotor performance of aged women.
2. Methods and Materials
This was a quasi-experimental study with Pre-test-Post-test design conducted in 2017 on 47 elderly women aged 60-70 years. The study participants were recruited from the Sports and Health Consultation Center of Qazvin Sports and Youth Department based on convenience sampling method. They were randomly assigned to 4 groups of functional exercises (EX), omega-3 supplementation (SUP), exercise+omega-3 supplementation (EX+SUP), and placebo. Inclusion criteria were the age of ≥60 years, not susceptible to omega-3 or fish supplements’ adverse effects, the ability to participate in training exercises, and no mobility limitations. To assess the readiness of subjects during training, the Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire (PAR-Q) was used.
The nutritional analysis of study subjects was examined before testing by N4 software to control the effect of nutrition on the results. The two groups of SUP and EX+SUP received two 2000 mg of omega-3 capsules (EPA 180 and DHA 120, Zahrawi Co.) daily for 8 weeks in the morning and night. The placebo group received two capsules containing 2% dextrose solution (Zakaria Co.). The functional exercise protocol was designed according to the American College of Sports Medicine instructions, consisting of 3 sessions/week (Saturday, Monday and Wednesday) for 50 min from 10:00 AM to 11:30 AM, and at least 1 hour after breakfast. Each session included a 10-min warm up, a 45-min strength and endurance training, and a 5-min cool down [5].
Psychomotor performance was measured using the Vienna test system which has acceptable validity. One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Multivariate Analysis of Covariance (MANCOVA) were used for analyzing the collected data. Descriptive statistics of study groups before and after the intervention are presented in Table 1.
3. Results
The Smirnov-Kolmogorov test results suggested the normal distribution of the obtained data (P>0.05). One-way ANOVA used for comparing the nutritional status of subjects reported no significant difference on the day before the pre-test phase (P>0.05). Groups EX, SUP, and EX-SUP demonstrated significant improvements in all psychomotor tests (P<0.05). By performing repeated measures ANOVA on three components in the 4 groups, a significant difference between the mean Pre-test and Post-test scores was observed (P<0.05). By removing the Pre-test effect, it was revealed that when a combination of omega-3 supplementation and functional exercises was used, the best results were achieved and their psychomotor performance was improved.
4. Conclusion
Any exercise intervention addressing aged people with mental challenges in terms of information processing and leading them to the problem-solving process can enhance their psychomotor performance. Based on the obtained results, the study participants’ response and precision of functional performance improved after exercise and supplementation interventions; this finding is very important in the motor control of aged people. This study reported improved psychomotor performance following functional exercising and omega-3 supplementation which should be considered by policymakers.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the International University of Imam Khomeini with the code of 17628.
Funding
This research has been extracted from the research project (No. 11821) funded by Imam Khomeini International University.
Authors contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: Morteza Taheri; Editing and Finalization: Khadijeh Irandoust.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Type of Study: Research |
Subject:
Geriatric
Received: 2018/10/10 | Accepted: 2019/01/23 | Published: 2019/05/15
Received: 2018/10/10 | Accepted: 2019/01/23 | Published: 2019/05/15
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |